gastrointestinal tuberculosis
Abdominal
tuberculosis • Tuberculous lymphadenitis - abdomen - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
Abdominal
tuberculosis • Gallbladder tuberculosis - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
Abdominal
tuberculosis • Disseminated tuberculous infection with miliary disease, lymphadenitis, and colitis - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
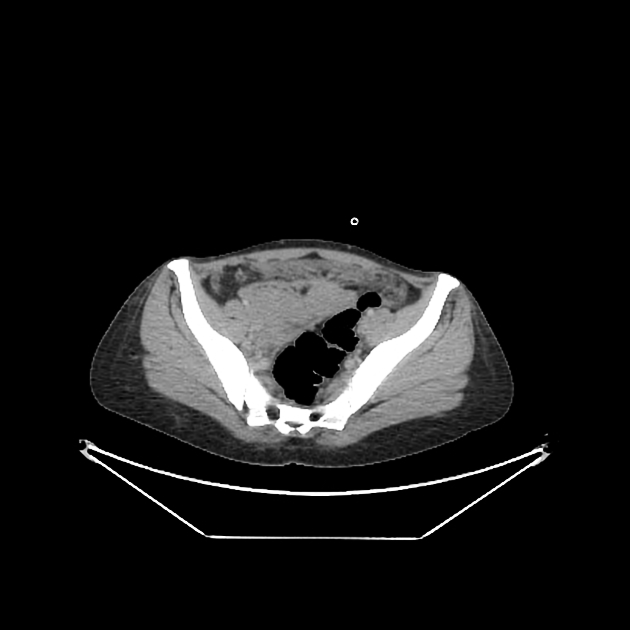
Abdominal
tuberculosis • Cerebral and abdominal tuberculosis (PET-CT) - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
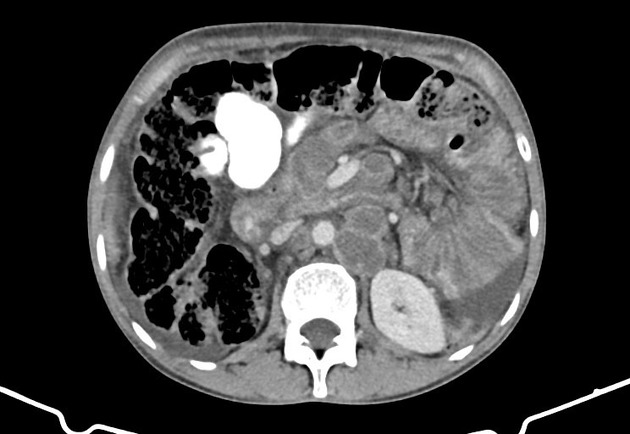
Abdominal
tuberculosis • Tuberculous lymphadenitis - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
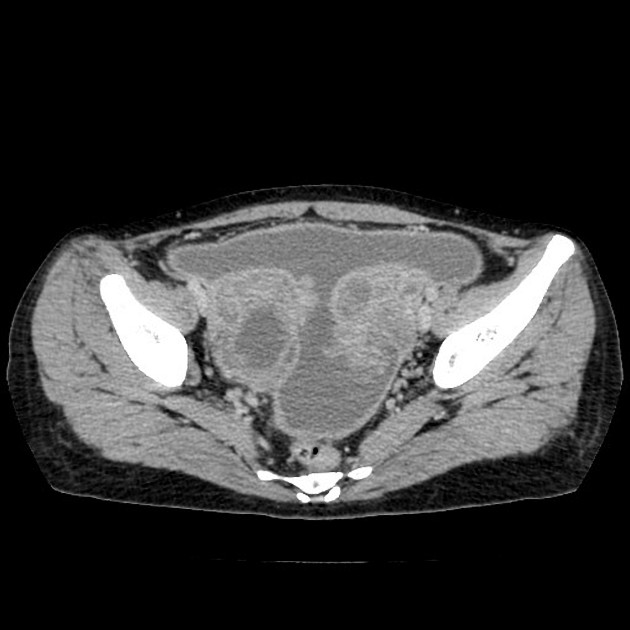
Tubo-ovarian
abscess • Tuberculous tubo-ovarian abscess and peritonitis - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
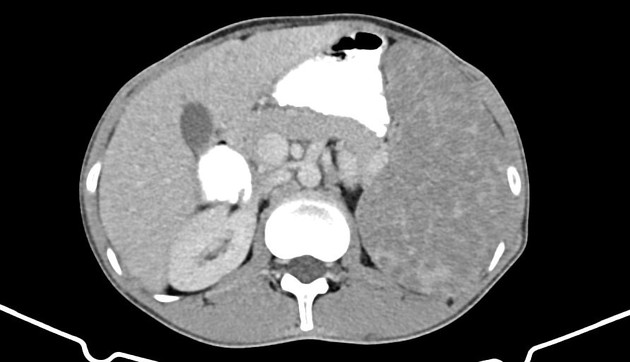
Splenic
granulomatous disease • Splenic and hepatic tuberculous granulomatosis - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
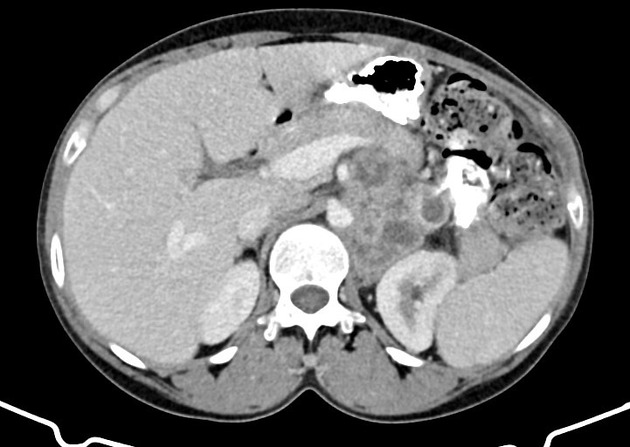
Abdominal
tuberculosis • Abdominal wall and retroperitoneal tuberculosis - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
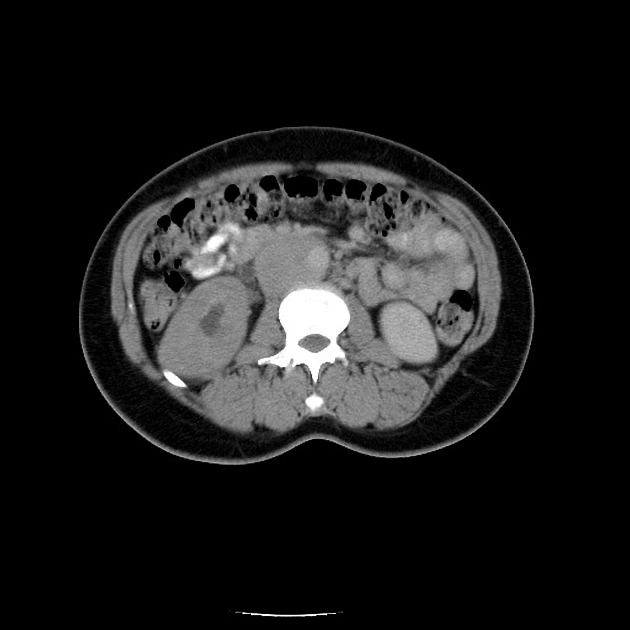
Tuberculosis
• Retroperitoneal tuberculosis resulting in renal obstruction - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
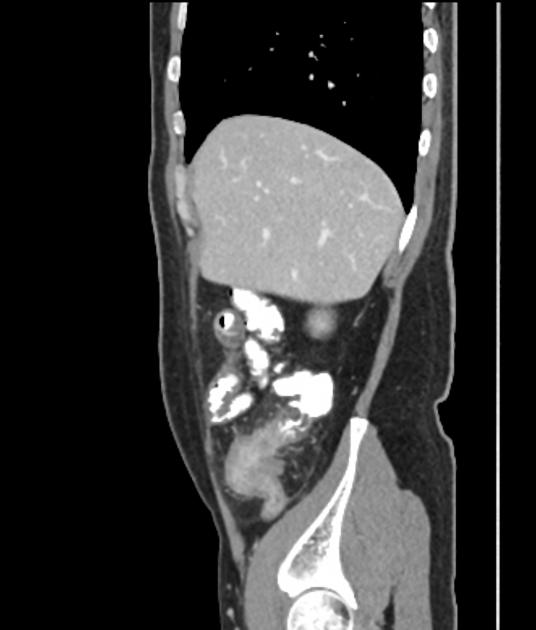
Abdominal
tuberculosis • Ileocecal tuberculosis and appendicitis - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
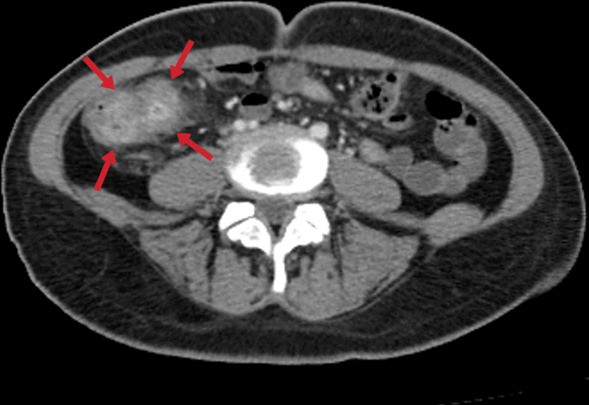
Extrapulmonary
tuberculosıs: an old but resurgent problem. A 31-year-old female. Contrast-enhanced CT image demonstrates diffuse-symmetric wall thickening and enhancement of the cecum with surrounding inflammatory changes (arrows)
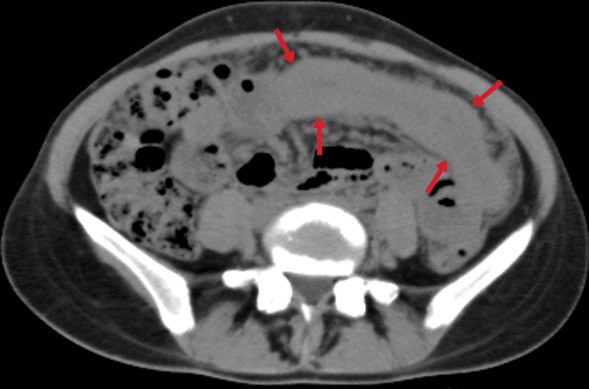
Extrapulmonary
tuberculosıs: an old but resurgent problem. Transverse CT image without intravenous contrast of a 24-year-old female. Diffuse-symmetric wall thickening of the ileal segment is noted (arrows). Ileal TB
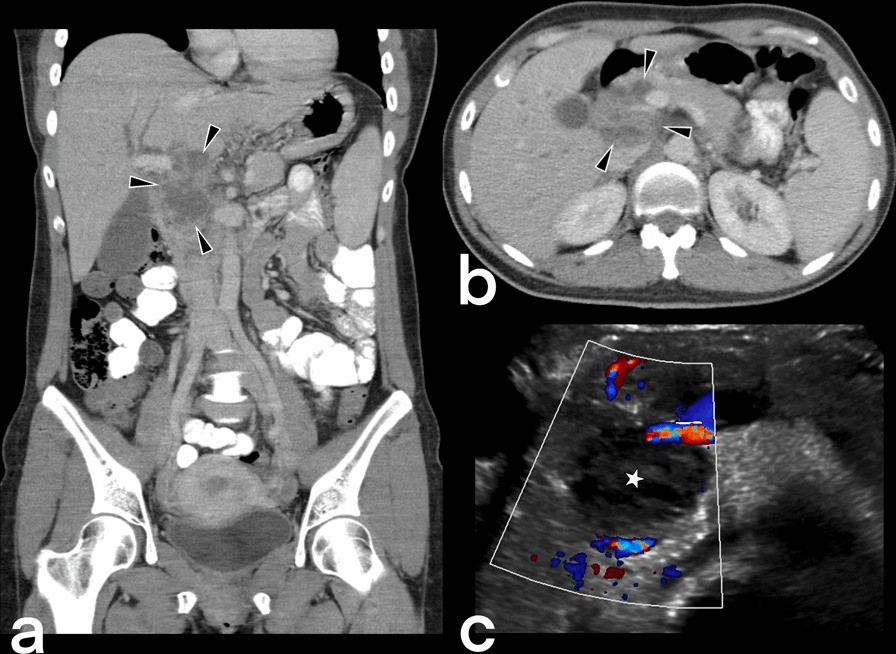
Extrapulmonary
tuberculosıs: an old but resurgent problem. A 40-year-old female. Contrast-enhancement CT scan (a, b) and Doppler ultrasonography (c) demonstrated a large heterogeneous cystic-necrotic mass in the head of the pancreas
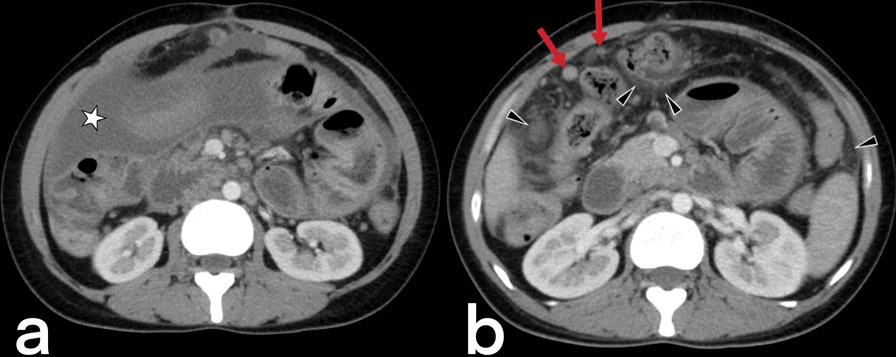
Extrapulmonary
tuberculosıs: an old but resurgent problem. A 33-year-old female. Axial post-contrast CT images (a, b) demonstrate omental nodularity, mesenteric fat stranding (arrowheads), and ascites (star). Intraabdominal lymphadenopathies are also evident (arrows) in image b
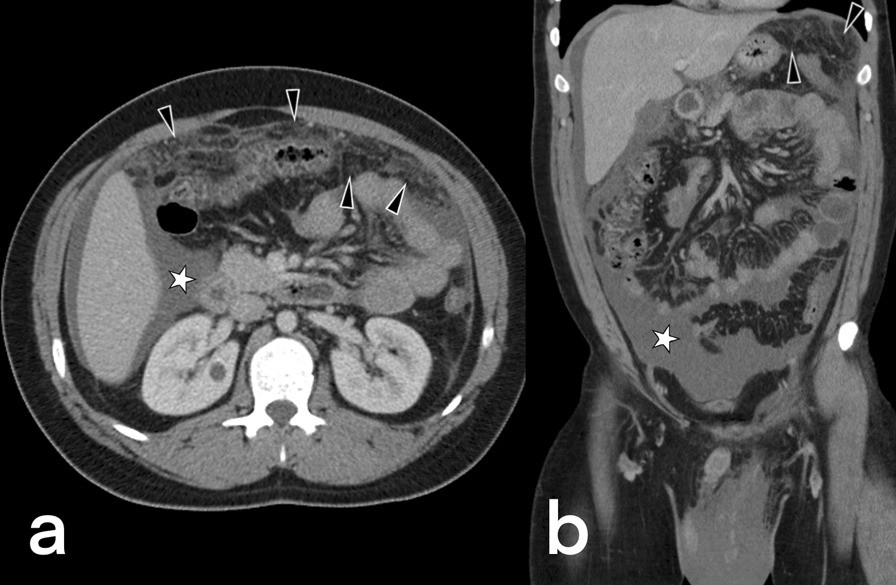
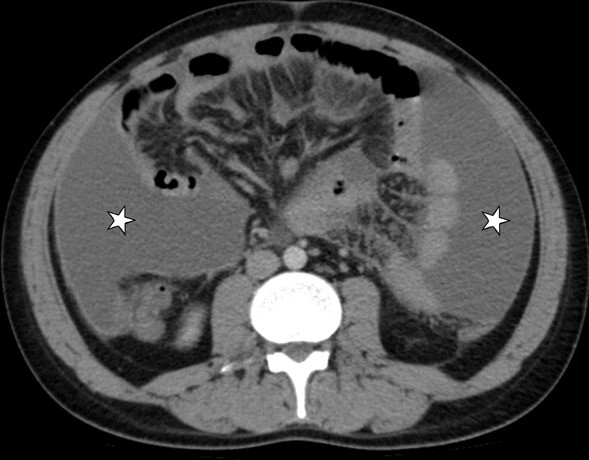
Extrapulmonary
tuberculosıs: an old but resurgent problem. A 24-year-old male patient. Axial (a) and coronal postcontrast CT (b) images show mesenteric striation (arrowheads) and ascites (star)
Extrapulmonary
tuberculosıs: an old but resurgent problem. Transverse CT image with intravenous contrast of a 29-year-old male. Massive ascites is indicated in the abdomen cavity (stars). The peritoneum"s thin linear contrast enhancement is also noted. Tuberculous peritonitis
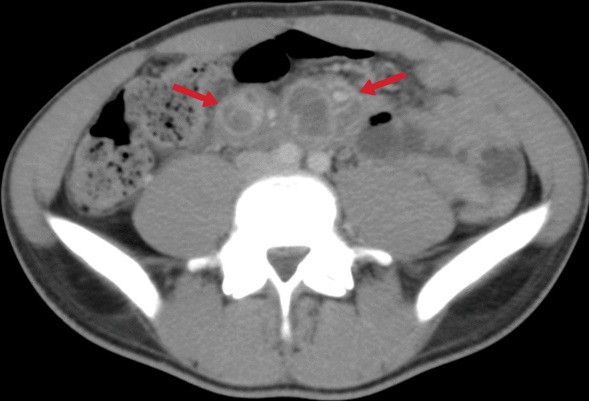
Extrapulmonary
tuberculosıs: an old but resurgent problem. A 19-year-old male. Post-contrast CT image shows multiple mesenteric lymphadenopathies with peripheral enhancement
Abdominal tuberculous can manifest in almost every abdominopelvic organ:
- gastrointestinal tuberculosis
- esophageal tuberculosis
- gastric tuberculosis
- duodenal tuberculosis
- jejunal and ileal tuberculosis
- ileocecal tuberculosis
- colorectal tuberculosis
- tuberculous peritonitis
- tubercular lymphadenopathy
- visceral tuberculosis
- hepatic tuberculosis
- gallbladder tuberculosis
- pancreatic tuberculosis
- splenic tuberculosis
- genitourinary tuberculosis
- renal tuberculosis
- bladder and ureteric tuberculosis
- prostatic tuberculosis
- scrotal tuberculosis (testes, epididymis, seminal vesicles, vas deferens)
- tuberculous pelvic inflammatory disease (female)
Pathology
There are three main pathways for tuberculous infection of the abdomen :
- ingestion of infected milk or sputum initially affects gastrointestinal tract mucosa, followed by the remainder of the bowel wall, regional lymph nodes and peritoneum
- haematogenous spread to the peritoneum, lymph nodes and solid viscera
- direct spread to the peritoneum, e.g. from skeletal tuberculosis via a psoas abscess
Siehe auch:
- Tuberkulose des Peritoneums
- Tuberkulose des Pankreas
- Tuberkulose des Ösophagus
- mesenteric panniculitis associated with abdominal tuberculous lymphadenitis
- intra-abdominal abscess due to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
- abdominelle tuberkulöse Lymphadenitis
und weiter:
- granulomatöse Peritonitis
- Fleischner sign (tuberculosis of ileocecal junction)
- duodenal tuberculosis
- peritoneal tuberculosis following infliximab therapy
- peritoneal tuberculosis: CT evaluation
- Tuberkulose des Peritoneums bei Kindern
- biliäre Tuberkulose
- Tuberkulose Nebenniere
- Peritonitis chronica fibrosa incapsulata
- Stierlin-Zeichen
- ileozökale Tuberkulose

 Assoziationen und Differentialdiagnosen zu intraabdominelle Tuberkulose:
Assoziationen und Differentialdiagnosen zu intraabdominelle Tuberkulose: