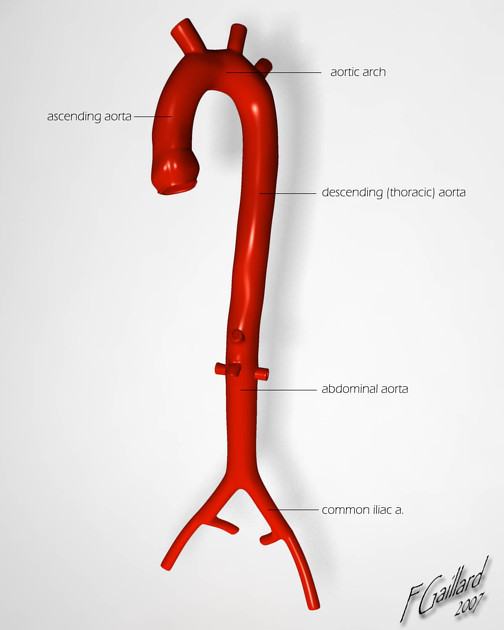
Abdominal aortic injury
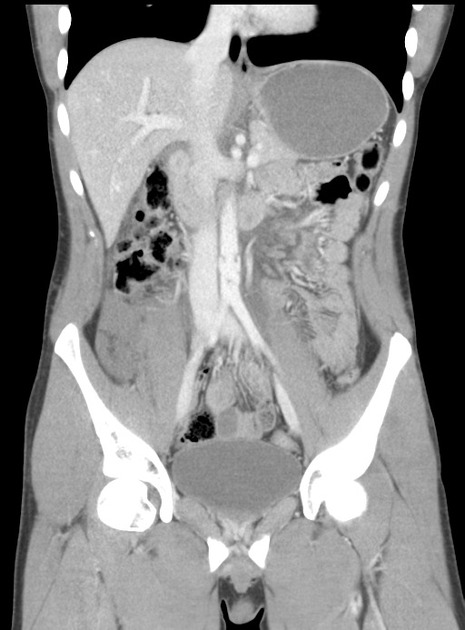
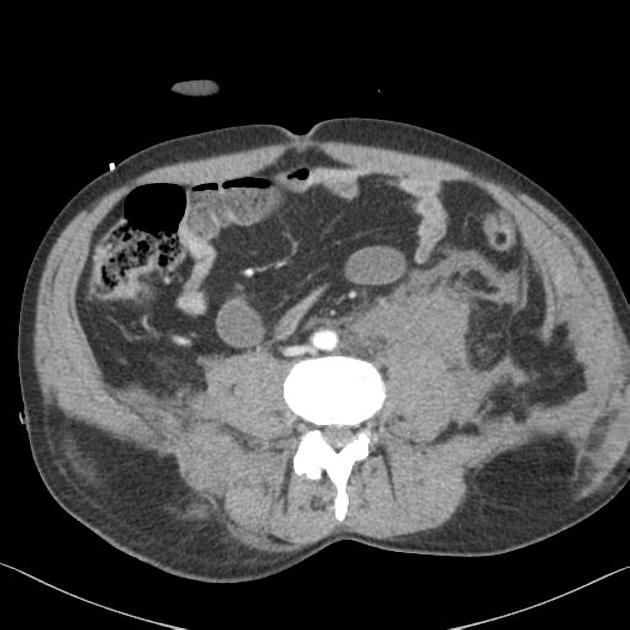
Abdominal aortic injuries are a very rare form of traumatic aortic injury and are much less common than thoracic aortic injury.
Epidemiology
Aortic injury occurs in <1% of blunt trauma patients, with abdominal aortic injury representing only ~5% of all aortic injuries . Males are more frequently injured, with the median age ~30 years .
Pathology
Abdominal aortic injuries are most commonly from a deceleration in motor vehicle accidents and range from intimal tears/flaps (minimal aortic injury), pseudoaneurysm to aortic transection . Aortic wall rupture can be due to branch avulsion .
Location
- level of the inferior mesenteric artery (~33%)
- level of renal arteries (~25%)
- inferior to the inferior mesenteric artery (~20%)
Etiology
- blunt trauma
- motor vehicle collisions (~70%)
- crush injuries (~20%)
- penetrating trauma
- gunshot injuries more than stabbing
- iatrogenic trauma
Associations
Associated traumatic injuries in blunt abdominal aortic injury include :
- retroperitoneal hematoma (50%)
- bowel and mesenteric injury, especially small bowel (up to 40%)
- lumbar spine fracture (~25%)
- pelvic fracture (~20%)
- splenic injury (~20%)
- thoracic aortic injury (<10%)
- inferior vena caval injury (<10%)
- renal and iliac artery injury
- hepatic, renal and pancreatic injury
Radiographic features
The radiographic features are not dissimilar to thoracic aortic injuries . The seatbelt sign is positive in ~35% of cases .
Treatment and prognosis
Most (~90%) abdominal aortic injuries are managed non-operatively. Those who require operative management, endovascular repair is more common . Mortality is reported at 30% .
Siehe auch:

 Assoziationen und Differentialdiagnosen zu Verletzungen der Aorta abdominalis:
Assoziationen und Differentialdiagnosen zu Verletzungen der Aorta abdominalis: