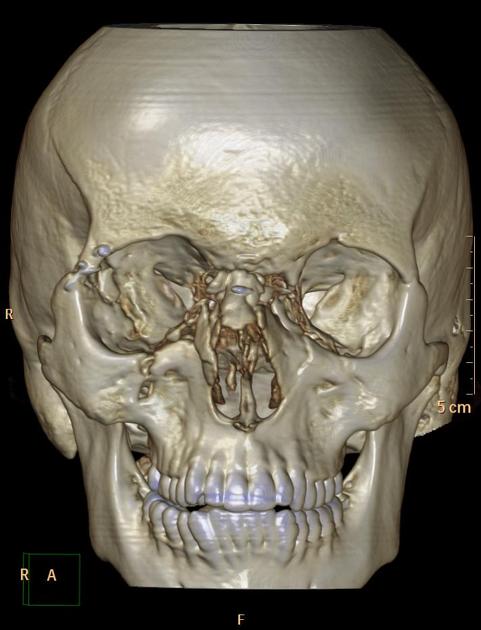
Naso-orbitoethmoid (NOE) complex fracture
Naso-orbitoethmoid
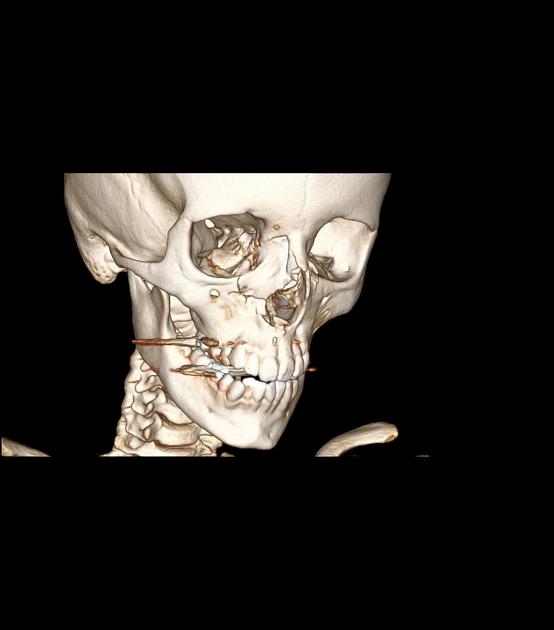
(NOE) complex fracture • Naso-orbitoethmoid (NOE) complex fracture - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
Naso-orbitoethmoid
(NOE) complex fracture • Nasoorbitoethmoid fracture - Ganzer Fall bei Radiopaedia
Naso-orbitoethmoid (NOE) fractures (also known as orbitoethmoid or nasoethmoidal complex fractures) are fractures which involve the central upper midface.
Pathology
Naso-orbitoethmoid fractures are caused by a high-impact force applied anteriorly to the nose and transmitted posteriorly through the ethmoid bone.
Associations
Associated injuries include:
- telecanthus secondary to medial canthal tendon injury
- nasolacrimal duct disruption and subsequent frontal mucocele formation
- orbital injuries and exophthalmos due to reduced intra-orbital volume
- cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea due to fracture through the cribriform plate
- epiphora secondary to nasolacrimal duct injury
Radiographic features
Comminution of both medial maxillary buttresses results in a pattern of fractures involving the nasal bones and septum, ethmoid sinuses, and medial orbital walls.
Classification
The Markowitz and Manson classification system categorizes fractures of the NOE complex as follows :
- type I: in which the medial canthal tendon is intact and connected to a single large fracture fragment
- type II: the fracture is comminuted, and the medial canthal tendon is attached to a single bone fragment
- type III: comminution extends to the medial canthal tendon insertion site on the anterior medial orbital wall at the level of the lacrimal fossa, with resultant avulsion of the tendon

